Tapered roller bearings (TRB bearings) are a type of bearing commonly used to handle radial and axial loads, especially playing a crucial role in the gearboxes of rail trains. Its unique structure enables it to effectively cope with high-load, high-speed rotating working environments. This article will provide a detailed introduction to the structure composition of TRB bearings and their application in railway train gearboxes, helping you gain a deeper understanding of their importance and advantages.
TRB bearings primarily consist of inner ring, cage, rolling elements, and outer ring.
Inner Ring (Conical Inner Ring)
The inner ring is the inner component of the bearing, usually fitted with the shaft, and acts as an inner sleeve mounted on the shaft. The inner hole of the inner ring is the raceway for the bearing rolling elements, ensuring effective contact between the tapered rollers and the inner ring, thereby bearing the load.
Cage (Tapered Roller Cage)
The cage is the part that holds the rolling elements, usually made of steel material, to maintain the spacing and relative position of the rolling elements, ensuring the stable operation of TRB bearings. The cage not only helps reduce friction but also enhances the bearing's durability.
Rolling Elements (Tapered Rollers)
The rolling elements are the parts in TRB bearings that bear the load and roll on the raceway, shaped like a cone. This design enables them to effectively bear axial and radial loads, adapting to various working conditions.
Outer Ring (Conical Outer Ring)
The outer ring is the outer component of the bearing, usually fitted with the external structure, acting as an outer sleeve mounted on the external structure. The outer surface of the outer ring is the raceway for the bearing rolling elements, directly participating in the load-bearing process.
The gearboxes of railway trains are usually installed at the bottom of the vehicle, acting as a crucial component of the transmission system. The gearbox is responsible for transmitting power and adjusting speed, ensuring the normal operation of EMU trains. Due to the high operating speed of trains, gearboxes are subjected to high-speed rotation and high-load pressure during operation. In such an environment, choosing the right type of bearing is particularly important.
TRB bearings, due to their special structural design, can bear both radial and axial loads simultaneously and have a certain self-aligning ability, making them very suitable for the output shaft position of gearboxes. The TRB bearing installed inside the gearbox fits tightly with the output shaft, supporting its rotational movement. Due to its excellent load-bearing capacity, the TRB bearing can effectively share the load generated by gear transmission, maintaining stability and durability under high-speed rotation.
The use of TRB bearings not only reduces wear and fatigue of bearing components but also extends the service life of the gearbox, enhancing the reliability and safety of the train. Therefore, choosing TRB bearings in the gearboxes of railway trains is very necessary and suitable.
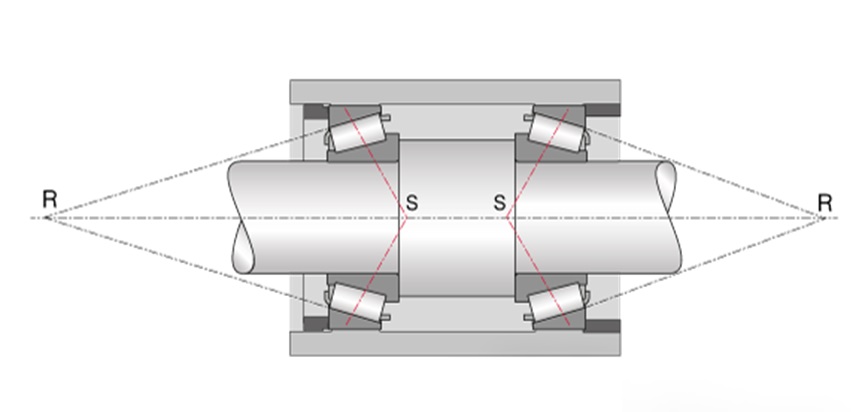
The TRB bearings on the gearbox are usually installed in an X-shaped layout, that is, the rollers of two bearings are arranged in an X shape. This layout is primarily used in applications that bear bi-directional radial loads and axial loads. The X-shaped layout not only provides higher axial and torsional stiffness but also effectively balances bi-directional loads, further enhancing the performance and longevity of TRB bearings.